In 2022, the world has seen the outbreak and spread of illnesses that were never considered a threat to most countries like monkeypox, and now the return of polio to the United States.
On September 9, the governor of New York declared a state of emergency for polio due to the evidence of spreading across the state in many counties like Nassau County, Sullivan County, Orange County, and Rockland County.
Even though the United States was declared free of polio in 1979, and the last case of wild poliovirus type was brought into the country by travelers in 1993, the new cases have raised the preoccupation of many people because of its effect on the human body and the post-polio syndrome.
But is polio a threat to the health of Americans? We will tell you everything you need to know in our blog.
What is Polio?
Polio, also called poliomyelitis, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. In most cases, people infected will not develop any visible symptoms or will have flu-like symptoms. There is also a slight possibility of developing severe symptoms like meningitis, paralytic symptoms, or permanent paralysis. This is known as paralytic polio or paralytic poliomyelitis.
Polio used to be one of the biggest fears in the United States in the 20th century and the years before 1955 when the inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) was developed and the polio immunization efforts started. This showed a violent decrease in the number of people infected in many countries around the world, which translated into fewer paralytic polio and polio deaths making the health benefits undeniable.
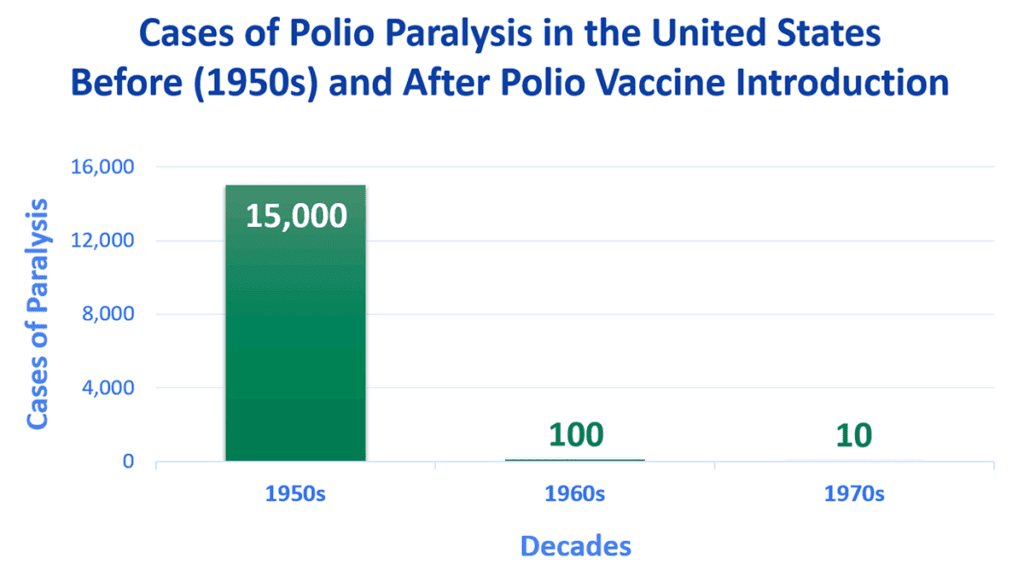
Nonetheless, there are still two endemic countries where the prevalence of polio has never ceased: Afghanistan and Pakistan.
What Are The Symptoms of Polio?
As mentioned above, most of the people infected will not experience any symptoms.
An infected person (around 1 in 4) can experience flu-like symptoms including:
- Sore Throat
- Muscle Weakness
- Fever
- Headache
- Stomach ache
These are temporary symptoms that can last from 2-5 days, and then they will disappear.
An infected person can also experience other effects of polio and severe symptoms affect the brain and spinal cord like:
- Meningitis consists of inflammation of the membranes (meninges) that surround the brain and spinal cord. 1-5 out of 100 people can experience this disease.
- Paralysis is the most severe symptom and it occurs in 1 out of 200 or 2000, depending on the virus type. The paralytic effects of polio can also vary from person to person and the post-polio syndrome (people who recover from the severe illness) can experience muscle pain, weakness, or permanent paralysis.
2-10 out of 100 people infected with the paralytic disease can die due to complications with the breathing muscles.
How is Polio Transmitted?
The transmission of polio is through person-to-person contact. It can happen when having contact with the feces of an infected person, or by consuming contaminated water or food.
Even though it is less common, the transmission of polio can also happen through droplets from a sneeze or cough of an infected person.
As mentioned above, polio is an illness that can be invisible in most cases or have temporary symptoms that can be confused with flu or colds, but even people infected that don’t show symptoms can infect other people, which makes spreading the illness easier.
How is Polio Treated?
Currently, there is no specific treatment for polio.
As mentioned above, mild and flu-like temporary symptoms will go away on their own between 2-5 days.
Nonetheless, there is no treatment to avoid the effects of paralytic poliomyelitis. The best way to treat polio is with prevention and polio immunization.
On the other hand, after experiencing the paralytic disease, health workers can restore to physical therapy to improve the effects of polio and post-polio syndrome.
Is There a Cure For Polio?
There is no cure for polio in existence, nor a treatment when facing the effects of post-polio syndrome which can include permanent paralysis. Recurrent therapy can help to improve the movement and weakness of the muscles, but there is no cure for the illness.
What Can I Do To Avoid Infection?
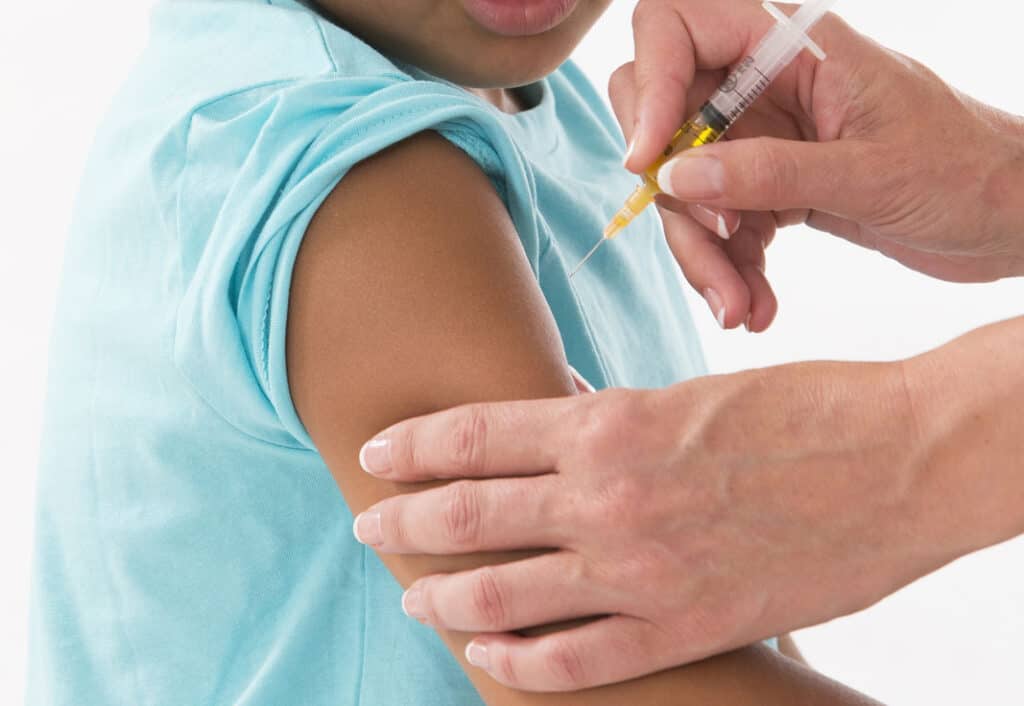
The best and proven way to avoid the infection of polio is with the poliovirus vaccine.
One of the advantages in the fight against the spread of the illness is that polio is a vaccine-preventable disease. With immunization, either with the inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) or oral polio vaccine (OPV) developed by Albert Sabin, a healthy person will be completely protected from paralytic symptoms and temporary symptoms.

Many health officials and organizations like CDC recommend that children, in the United States and other countries, get four doses of the poliovirus vaccine to protect against the illness.
If an adult went through the entire process of vaccination as a child, there would be no need for immunization. It may also be the case of receiving a single booster shot if the individual is traveling at a high risk of exposure to polio zone.
If the process wasn’t completed or started in childhood and the adult is at a high risk of exposure to polio zone, immunization should happen to avoid infection.
In the United States, the vaccine used for polio immunization is the inactivated polio vaccine which is very safe and effective. The oral poliovirus vaccine, developed by Albert Sabin, is no longer licensed in the United States, but it is used in other countries.
Can Someone Recover From Polio?
It is possible to recover from polio when a person is affected with serve and paralytic symptoms. Nonetheless, even children or young adults who suffered from infantile paralysis from polio and recover can become weakened again due to the post-polio syndrome.
The post-polio syndrome has a 25-40% rate of recurrence, and the symptoms occur between 15-30 years after the paralytic polio.
The symptoms will look similar to polio, with muscle weakness, joint pain, and tiredness, and the severity will vary from person to person. The post-polio syndrome is not life-threatening, but it can cause discomfort to the person affected.
There is a chance to recover, and even not suffer from post-polio syndrome, but polio is a vaccine-preventable disease, and we recommend prevention with vaccination with the oral poliovirus vaccine or the inactivated polio vaccine, depending on the country of your residence.
Is Polio The New Threat To Our Health?
With the new polio outbreaks found in New York in Rockland County, Orange County, Sullivan County, and Nassau County, we understand the concern, even more after the events of the last three years and the spread of respiratory illness and quarantine.
We can’t deny the effects polio can have after a healthy person is infected, but most Americans have been vaccinated against this illness thanks to routine immunization programs, and the polio immunization efforts started in 1955.
These immunization efforts prepared the United States for possible polio outbreaks, and at the same time, eliminated possible infantile paralysis, polio patients and permanent paralysis, and post-polio syndrome. We, as Americans, have lived with the benefits of eradication.
If you were vaccinated as a child following the CDC recommendations, there is nothing to worry about.
If you are an adult who was not fully vaccinated against polio and is at a high risk of exposure to polio zone, you should consider getting vaccinated.

Polio is a vaccine-preventable disease and you should take advantage of this.
If you are worried or want to know more about polio, you can contact a trusted health worker that will help you fully understand your situation

Recent Comments